

Pancreatic cancer
According to statistics, only a small percentage of patients with pancreatic cancer have a 5-year survival rate. The disease is further complicated by the fact that malignant neoplasm is rarely detected at an early stage.
Well, the main symptoms of pancreatic cancer can be divided into three groups: obstruction, compression, and intoxication.
Obstruction (blockage) happens when the tumor increases in size, which blocks the pancreatic duct, common bile duct, duodenum and compresses the splenic vein. This is what causes the development of biliary hypertension and, as a consequence of obstructive jaundice, renal and hepatic failure. Compression develops due to nerve suppression that the tumor causes. And intoxication occurs due to "waste products" of cancer cells activity in the tissues and blood.
In this regard, the main symptoms of pancreatic cancer are:
Pain
Obstructive jaundice
Itchy skin (manifests itself based on jaundice due to irritation of skin receptors with bile acids)
Weight loss (belongs both to intoxication symptoms and symptoms of digestion disorders)
Inability to eat normally, due to nausea, heartburn, and possible bowel dysfunctions
The development of diabetes, an enlarged spleen, an enlarged gallbladder
Pancreatic cancer is insidious: often the first symptoms appear only in the late stages when the tumor suppresses the neighboring organs.
Types:
Specialists identify several pancreatic cancer types. About 90% of all pancreatic cancer types originate in exocrine cells (neoplasms of the mucus-secreting gland).
There are such pancreatic cancer types as neuroendocrine tumors, manifesting as bronchial spasms, intestinal ulcers, and fibrosis. These types of pancreatic cancer are also referred to as islet cell cancers. About 5% of all types of cancer of the pancreas are considered neuroendocrine tumors.
Treatment:
Pancreatic cancer treatment is carried out in a combined course, using several methods at once.
The pancreatic cancer treatments are:
Surgery implies not only the resection of affected part of the organ itself but also the lymph nodes adjacent to it, a duodenum section, and stomach affected by the process. Surgery isn’t indicated for pancreatic cancer with metastases.
None-radical surgery. Typically, these are endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, and anastomosis.
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is applied both as an independent method and as an additional method before and after surgery. In the case of preoperative chemotherapy, the main goal is to reduce the size of the tumor; postoperative chemotherapy helps to get rid of the remaining cancer cells to prevent the tumor from spreading.
Radiation therapy. It is also indicated in the postoperative period to prevent the development of new foci of cancer. Unlike chemotherapy, which also affects healthy cells, radiation treatment is directed more locally, which avoids damage to other organs and cells.
palliative cancer treatments for stage 4 pancreatic cancer may include the following procedures:
Pain management with non-narcotic or narcotic analgesics.
Supportive therapy that helps to cope with side effects and better reschedule chemotherapy.
Fight against exhaustion. The doctor evaluates the patient's nutritional status and prescribes an optimal diet.
Restoring the patency of the stomach by creating anastomosis: a section of the intestine is sutured to the wall of the stomach and a hole is formed between them.
Fight against ascites.
____________________________________________________________________
Gall bladder cancer
Overview:
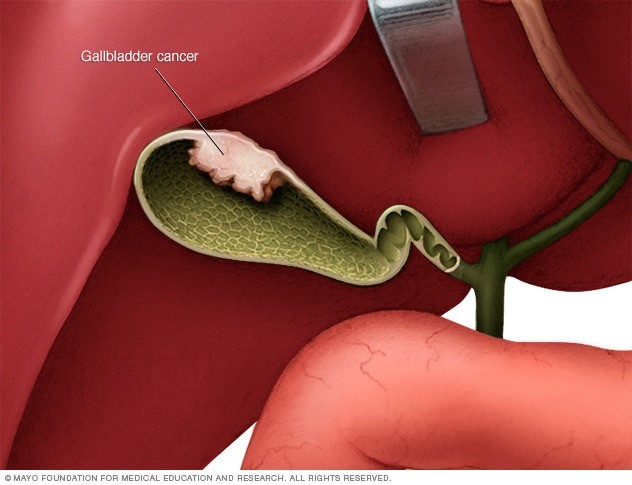
Gallbladder cancer is a growth of cells that begins in the gallbladder.
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of the belly, just beneath the liver. The gallbladder stores a fluid called bile that the liver makes to digest food.
In cancer cells, the DNA changes give different instructions. The changes tell the cancer cells to make many more cells quickly. The cancer cells might form a mass called a tumor. The tumor can grow to invade and destroy healthy body tissue. In time, cancer cells can break away and spread to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads, it's called metastatic cancer.
مؤسسة شفا الأورمان المُشهره بوزارة التضامن الاجتماعي برقم 5859 لسنة 2016
جميع الحقوق محفوظة مستشفي شفاء الأورمان - صعيد بلا سرطان © 2024